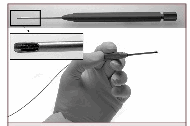
Laser Fiber
Usefulness of the CO2 flexible laser fiber in the removal of intracranial meningiomas.
The experience of the San Filippo Neri Hospital in Rome (Luciano Mastronardi)
Introduction:
Primitive intracranial tumors are relatively uncommon: in Italy there are about 10 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Most of them originate from nutritional and support tissues of the brain in which are located glial cells and nervous fibers (gliomas), the meninges (meningiomas) and the myelin sheath of the cranial nerves (neuromas). The brain tumor does not metastasize, except in rare cases. The ” benignity” of some intracranial tumors does not always correspond to the possibility of healing. In fact, in some locations, even partial removal of the tumor can be very risky for the non-negligible mortality (as in the case of lesions adjacent to or growing into the brain stem), or the possible morbidity, as in the case of tumors that arise in the proximity of “eloquent” brain areas, (that express a particular function, such as speech or movement) of the cranial nerves (optic, oculomotor, trigeminal, facial, acoustic, vagus, etc.) or of large arteries and veins of vital relevance.
The main objective of the modern Neurosurgical oncology consists of the maximal removal of the neoplasm with minimization of complications. Various tools have improved the performances in the surgical removal of brain tumors in recent years:
1. acquisition and processing of images both pre- and intraoperative (thin-slice CT, MRI, functional MRI and tractography, navigational systems, 2D and 3D endoscopy, ultrasounds).
2. increasingly sophisticated surgical equipment (microscope integrated with navigation, fine bipolar forceps, microsurgical instruments dedicated for each procedure, ultrasonic aspirators, laser fibers).
Among these instruments essential for the successful of the surgical procedure, an increasingly relevant role has nowadays the CO2 flexible laser fiber, which is used directly by the surgeon hand (unlike the old remote-controlled laser) as an essential aid in the removal of brain and spinal cord tumors, particularly meningiomas. International experiences and our experience in San Filippo Neri in Rome are very encouraging.
Objectives :
The CO2 laser has been proven effective for years in the armamentarium used by neurosurgeons for the removal of brain tumors, especially for benign neoplasms of skull base and convexity, such as meningiomas and neuromas. Recently, the possibility of using the CO2 laser with flexible fiber hand-held (directly used by the surgeon) has relaunched its use. On the basis of the first international experience we started using the CO2 laser in the procedures for removal of selected intracranial tumors, with the functions of cutting, coagulating and vaporizing the tumor, observing some peculiarities and evaluating its effectiveness and safety.
Materials and methods :
Together with the microsurgical instruments, a variety of dedicated bipolars and an ultrasonic aspirator, around 4 years ago we have started to use the CO2 flexible laser fiber in the removal of selected intracranial tumors. In particular, we have operated with this instrument over 60 intracranial tumors, 36 of which were meningiomas (2/3 supratentorial and 1/3 in the posterior cranial fossa).
Results :
The flexible CO2 laser fiber has been proven safe and effective. The total excision was possible in 16 meningiomas, subtotal in others 16 (with small residuals in areas at risk, in order to avoid significant neurological damages) and partial in 4 giant meningiomas in elderly patients.
Regarding the CO2 laser, the average percentage rates of cutting / coagulation / vaporization were 55/28/17 for extra-axial tumors (meningiomas and neuromas), compared to 15/65/20 for other tumors. This is justified by the fibrous and more compact nature of meningiomas and their vascularization, which makes more difficult to remove it while using traditional instruments. The CO2 laser has been proven very useful for vaporization and coagulation of the dural attachment of meningiomas too, especially at the level of the skull base.
Conclusions :
Observing the necessary technical-surgical procedures and the correct indications, the flexible CO2 laser represents a valuable aid in the microsurgical removal of intracranial tumors, especially meningiomas, allowing to cut the tumor capsule, to coagulate pathological newly formed microvessels, and to vaporize, debulking the mass and removing the dural attachement of meningioma.
Our results are in line with international experience and literature.
References :
http://www.omni-guide.com/surgeons-neurosurgery-and-spine.htm
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1w9L_DpdApU
Attachments :